What are regulated activities in CQC compliance?
- Dental practices are required to register with the CQC if they provide:
- Treatment of diseases, disorders, or injuries
- Diagnostic and screening procedures
- Surgical procedures
Introduced on 1st April 2009 under the Health and Social Care Act 2008, the CQC ensures that healthcare providers adhere to regulations. An updated set of regulations, The Health and Social Care Act 2008 (Regulated Activities) Regulations 2015, came into effect on 1st April 2015, meaning dental practices must comply with these laws.
Ongoing Compliance in Dental Practices
Compliance is not a one-off task; it is an ongoing commitment to ensure the continuous delivery of safe, high-quality care. This is achieved through everyday adherence to regulations and by regularly updating staff knowledge and skills. Even temporary staff, such as locum dental care professionals, must meet compliance standards. Having a compliance checklist can be a useful tool to ensure all staff members are adhering to these regulations.
What Does the CQC Look For?
The CQC assesses dental practices using its Key Lines of Enquiry (KLOE) framework, which focuses on answering five key questions:
- Are services safe?
- Are services effective?
- Are services caring?
- Are services responsive to people’s needs?
- Are services well-led?
Each question is supported by a set of quality statements, which dental practices are expected to meet.
Are Services Safe?
- Learning when things go wrong
- Safeguarding from abuse
- Infection control
- Safe staffing levels
- Medicines management
- Creating a safe environment
Are Services Effective?
- Delivering evidence-based care
- Staff skills and knowledge
- Assessing patient needs
- Consent to treatment
- Collaboration among staff and services
Are Services Caring?
- Compassion, dignity, and respect
- Treating patients as individuals
- Promoting independence and choice
- Staff well-being and support
Are Services Responsive?
- Person-centred care
- Continuity of care and service integration
- Equity in access and outcomes
- Planning for future care needs
Are Services Well-Led?
- Compassionate, inclusive leadership
- Encouraging staff to speak up
- Equality, diversity, and inclusion in the workforce
- Sustainability and continuous improvement
- CQC evidence collection process
To evaluate a dental practice, the CQC gathers evidence from a range of sources. This evidence comes from both onsite and offsite assessments, covering six main categories:
People’s experiences: CQC gathers feedback from patients and their families via phone calls, surveys, and public reviews.
Staff feedback: Interviews, surveys, and feedback from staff members and leaders.
Partner feedback: Input from commissioners, professional regulators, and local organisations.
Onsite inspections: CQC inspectors visit the practice to observe care delivery and inspect the premises.
Processes: Evaluation of systems in place, such as safety incident management and patient record keeping.
Outcomes: Data on infection control, vaccination rates, and prescribing patterns.
How Does CQC Rate Dental Practices?
Following an inspection, the CQC assigns a rating for each of the five key questions and provides an overall rating. Practices are graded as:
- Outstanding
- Good
- Requires Improvement
- Inadequate
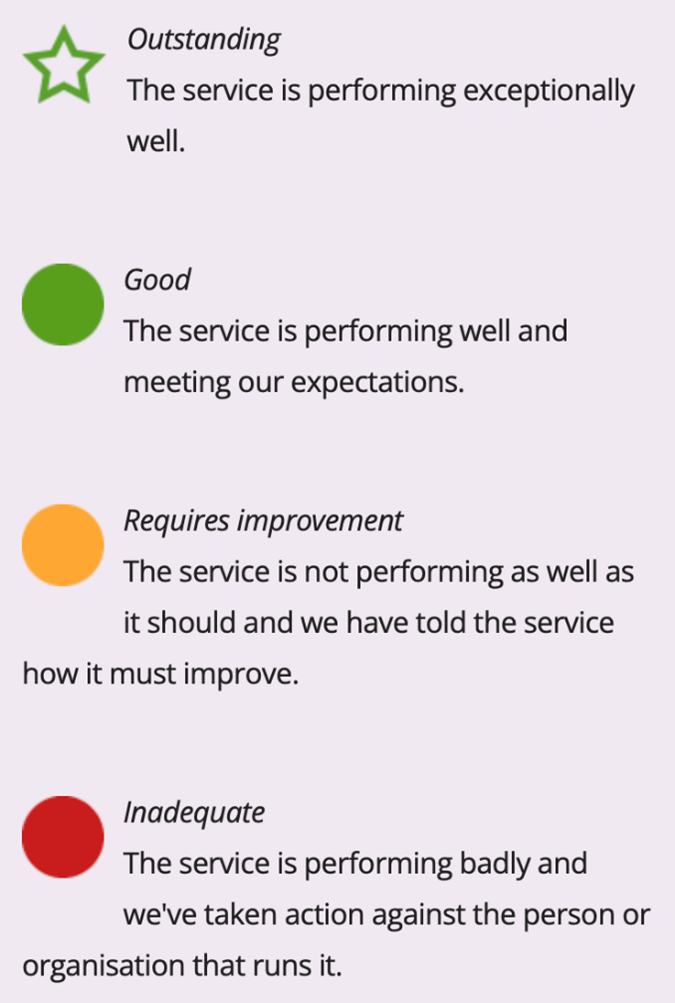
Image source: Ratings - CQC
These ratings help dental practices understand their current compliance level and identify areas for improvement.
In Summary The CQC plays a crucial role in ensuring that dental practices meet the required standards of care. By focusing on the five key questions and gathering evidence from multiple sources, the CQC provides an objective assessment of a practice’s performance. It is vital for dental practices to stay compliant, not only for legal reasons but to ensure the best care for their patients and a safe environment for their staff. Download our FREE locum first day induction checklist here.


